Glide Resource体系
Resource是Glide加载各种资源统一抽象化,从而在内部表现为统一的格式。
接口定义:
package com.bumptech.glide.load.engine;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
/**
* A resource interface that wraps a particular type so that it can be pooled and reused.
*
* @param <Z> The type of resource wrapped by this class.
*/
public interface Resource<Z> {
/**
* Returns the {@link Class} of the wrapped resource.
*/
@NonNull
Class<Z> getResourceClass();
/**
* Returns an instance of the wrapped resource.
*
* <p> Note - This does not have to be the same instance of the wrapped resource class and in fact
* it is often appropriate to return a new instance for each call. For example,
* {@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable Drawable}s should only be used by a single
* {@link android.view.View View} at a time so each call to this method for Resources that wrap
* {@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable Drawable}s should always return a new
* {@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable Drawable}. </p>
*/
@NonNull
Z get();
/**
* Returns the size in bytes of the wrapped resource to use to determine how much of the memory
* cache this resource uses.
*/
int getSize();
/**
* Cleans up and recycles internal resources.
*
* <p> It is only safe to call this method if there are no current resource consumers and if this
* method has not yet been called. Typically this occurs at one of two times:
* <ul>
* <li>During a resource load when the resource is transformed or transcoded before any consumer
* have ever had access to this resource</li>
* <li>After all consumers have released this resource and it has been evicted from the cache
* </li>
* </ul>
*
* For most users of this class, the only time this method should ever be called is during
* transformations or transcoders, the framework will call this method when all consumers have
* released this resource and it has been evicted from the cache. </p>
*/
void recycle();
}
它的整个体系:
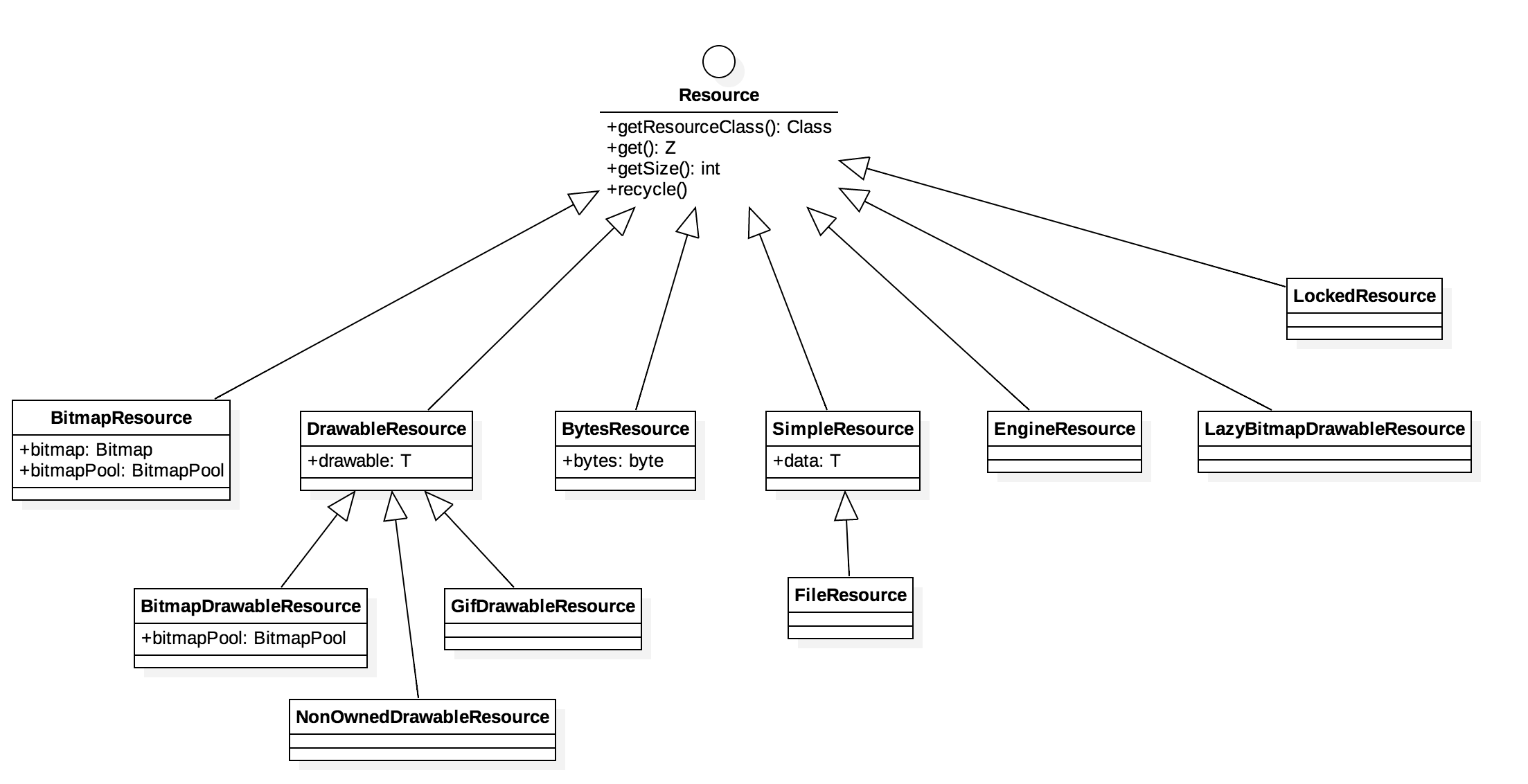
BitmapResource
整个就是对Bitmap的包装。注意2点:
1. bitmap的大小计算
public static int getBitmapByteSize(@NonNull Bitmap bitmap) {
// The return value of getAllocationByteCount silently changes for recycled bitmaps from the
// internal buffer size to row bytes * height. To avoid random inconsistencies in caches, we
// instead assert here.
if (bitmap.isRecycled()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot obtain size for recycled Bitmap: " + bitmap
+ "[" + bitmap.getWidth() + "x" + bitmap.getHeight() + "] " + bitmap.getConfig());
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
// Workaround for KitKat initial release NPE in Bitmap, fixed in MR1. See issue #148.
try {
return bitmap.getAllocationByteCount();
} catch (@SuppressWarnings("PMD.AvoidCatchingNPE") NullPointerException e) {
// Do nothing.
}
}
return bitmap.getHeight() * bitmap.getRowBytes();
}
2. BitmapPool
为了以后更方便的使用BitmapResource,它在回收的时候其实是放入了BitmapPool池中。
@Override
public void recycle() {
bitmapPool.put(bitmap);
}
Pool池的内容将在后面的文章中分析。
SimpleResource
它的作用是对于那些资源对象,我们不知道大小,并且不能回收或关闭。
FileResource
它是SimpleResource对象的具体实现者。
DrawableResource
这个是抽象类,代表的是所有Drawable的子对象。
Drawable就是一个可绘制的对象,里面保存的是可以绘制的数据,其可能是一张位图(BitmapDrawable),也可能是一个图形(ShapeDrawable),还可能只是一个颜色(ColorDrawable)等。
Drawable主要的功能就是给canvas上绘制图形,通过方法public void draw(Canvas canvas)操作。
这里主要的知识点:
public final T get() {
@Nullable ConstantState state = drawable.getConstantState();
if (state == null) {
return drawable;
}
// Drawables contain temporary state related to how they're being displayed
// (alpha, color filter etc), so return a new copy each time.
// If we ever return the original drawable, it's temporary state may be changed
// and subsequent copies may end up with that temporary state. See #276.
return (T) state.newDrawable();
}
什么是ConstantState?
同一个drawable可能会被使用在很多不同的地方,android系统为了优化内存,对drawable抽闲出了共用的状态(即Constant state),这样虽然是在使用不同的Drawable对象,但是这些不同的对象包含了一些共用的属性。
下图展现了view、Drawable和constant state的关系:

上面的优化是对同一个资源创建Drawable才有的优化。
ConstantState带来的问题
ConstantState优化了内存上的消耗,但是会引发修改一个地方,导致所有同一个资源的地方也同时内修改了的问题。
大家可以试下如下的代码:
Drawable star = getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.test);
star.setAlpha(10);
((ImageView) findViewById(R.id.one)).setImageDrawable(star);
Drawable star2 = getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.test);
((ImageView) findViewById(R.id.one)).setImageDrawable(star2);
会发现,我只想修改图片1的透明度,但是图片2的透明度也发生了改变,这其实不是我们想要的,而导致这样的问题的是ConstantState造成的。
如何解决呢?
drawable为我们提供了解决mutate()方法,就是对constant state进行一次拷贝,打破仅有一份constant state的束缚。

mutate()是这样定义的:
/**
* Make this drawable mutable. This operation cannot be reversed. A mutable
* drawable is guaranteed to not share its state with any other drawable.
* This is especially useful when you need to modify properties of drawables
* loaded from resources. By default, all drawables instances loaded from
* the same resource share a common state; if you modify the state of one
* instance, all the other instances will receive the same modification.
*
* Calling this method on a mutable Drawable will have no effect.
*
* @return This drawable.
* @see ConstantState
* @see #getConstantState()
*/
public @NonNull Drawable mutate() {
return this;
}
ConstantState接口的定义
public static abstract class ConstantState {
/**
* 从ConstantState创建新的Drawable对象
*/
public abstract @NonNull Drawable newDrawable();
/**
* 带上特定资源的,从ConstantState创建新的Drawable对象, 适合有density-dependent属性的具体实现者
*/
public @NonNull Drawable newDrawable(@Nullable Resources res) {
return newDrawable();
}
/**
* 带上特定资源的和主题,从ConstantState创建新的Drawable对象, 适合有theme-dependent属性的具体实现者
*/
public @NonNull Drawable newDrawable(@Nullable Resources res, @Nullable @SuppressWarnings("unused") Theme theme) {
return newDrawable(res);
}
/**
* constant state是否可以有theme
*/
public boolean canApplyTheme() {
return false;
}
public abstract @Config int getChangingConfigurations();
}
一个实现了ConstantState的例子
BitmapDrawable是Drawable的一个实现者,并且它实现了ConstantState接口:
final static class BitmapState extends ConstantState {
final Paint mPaint;
// Values loaded during inflation.
int[] mThemeAttrs = null;
Bitmap mBitmap = null;
ColorStateList mTint = null;
Mode mTintMode = DEFAULT_TINT_MODE;
int mGravity = Gravity.FILL;
float mBaseAlpha = 1.0f;
Shader.TileMode mTileModeX = null;
Shader.TileMode mTileModeY = null;
// The density to use when looking up the bitmap in Resources. A value of 0 means use
// the system's density.
int mSrcDensityOverride = 0;
// The density at which to render the bitmap.
int mTargetDensity = DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT;
boolean mAutoMirrored = false;
@Config int mChangingConfigurations;
boolean mRebuildShader;
BitmapState(Bitmap bitmap) {
mBitmap = bitmap;
mPaint = new Paint(DEFAULT_PAINT_FLAGS);
}
BitmapState(BitmapState bitmapState) {
mBitmap = bitmapState.mBitmap;
mTint = bitmapState.mTint;
mTintMode = bitmapState.mTintMode;
mThemeAttrs = bitmapState.mThemeAttrs;
mChangingConfigurations = bitmapState.mChangingConfigurations;
mGravity = bitmapState.mGravity;
mTileModeX = bitmapState.mTileModeX;
mTileModeY = bitmapState.mTileModeY;
mSrcDensityOverride = bitmapState.mSrcDensityOverride;
mTargetDensity = bitmapState.mTargetDensity;
mBaseAlpha = bitmapState.mBaseAlpha;
mPaint = new Paint(bitmapState.mPaint);
mRebuildShader = bitmapState.mRebuildShader;
mAutoMirrored = bitmapState.mAutoMirrored;
}
@Override
public boolean canApplyTheme() {
return mThemeAttrs != null || mTint != null && mTint.canApplyTheme();
}
@Override
public Drawable newDrawable() {
return new BitmapDrawable(this, null);
}
@Override
public Drawable newDrawable(Resources res) {
return new BitmapDrawable(this, res);
}
@Override
public @Config int getChangingConfigurations() {
return mChangingConfigurations
| (mTint != null ? mTint.getChangingConfigurations() : 0);
}
}
BitmapDrawable对应实现的mutate()方法:
/**
* A mutable BitmapDrawable still shares its Bitmap with any other Drawable
* that comes from the same resource.
*
* @return This drawable.
*/
@Override
public Drawable mutate() {
if (!mMutated && super.mutate() == this) {
mBitmapState = new BitmapState(mBitmapState);
mMutated = true;
}
return this;
}
BitmapDrawableResource
GifDrawableResource
专门针对gif的Drawable对象
NonOwnedDrawableResource
不关心Drawable大小,并且对于资源的回收是否有好处也不确定。
LockedResource
相当于给资源加了个锁,只有在锁调用了unlock之后才能真正执行资源的回收,否则会一直阻塞。
LockedResource里维护了一个对象池,这个在FactoryPools类专门介绍。
它的使用:
final class LockedResource<Z> implements Resource<Z>,
FactoryPools.Poolable {
private static final Pools.Pool<LockedResource<?>> POOL = FactoryPools.threadSafe(20,
new FactoryPools.Factory<LockedResource<?>>() {
@Override
public LockedResource<?> create() {
return new LockedResource<Object>();
}
});
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@NonNull
static <Z> LockedResource<Z> obtain(Resource<Z> resource) {
LockedResource<Z> result = Preconditions.checkNotNull((LockedResource<Z>) POOL.acquire());
result.init(resource);
return result;
}
synchronized void unlock() {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
if (!isLocked) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already unlocked");
}
this.isLocked = false;
if (isRecycled) {
recycle();
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void recycle() {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
this.isRecycled = true;
if (!isLocked) {
toWrap.recycle();
release();
}
}
}
EngineResource
带引用计数的的资源,具体的使用暂时不清楚。