ListView 和 RecycleView的缓存机制
ListView的缓存机制
ListView的缓存实现主要是靠着RecycleBin去实现的,而RecycleBin里又是有2个数组型的数据结构去存储这些view。
- mActiveViews
- mScrapViews

实际的源码上:
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft,
boolean selected) {
View child;
if (!mDataChanged) {
// Try to use an existing view for this position
child = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (child != null) {
// Found it -- we're using an existing child
// This just needs to be positioned
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
return child;
}
}
// Make a new view for this position, or convert an unused view if possible
child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
// This needs to be positioned and measured
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}
如果getActiveView()不为空,则直接调用setupChild()进行view的布局,而不用调getView()了。
而getActiveView()为空,则要进入到obtainView()方法里,这个就是去获取view。
obtainView源码如下:
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] isScrap) {
...
final View scrapView = mRecycler.getScrapView(position);
final View child = mAdapter.getView(position, scrapView, this);
if (scrapView != null) {
if (child != scrapView) {
// Failed to re-bind the data, return scrap to the heap.
mRecycler.addScrapView(scrapView, position);
} else {
isScrap[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
child.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
}
...
return child;
}
具体的流程的图:

RecyleView的缓存机制
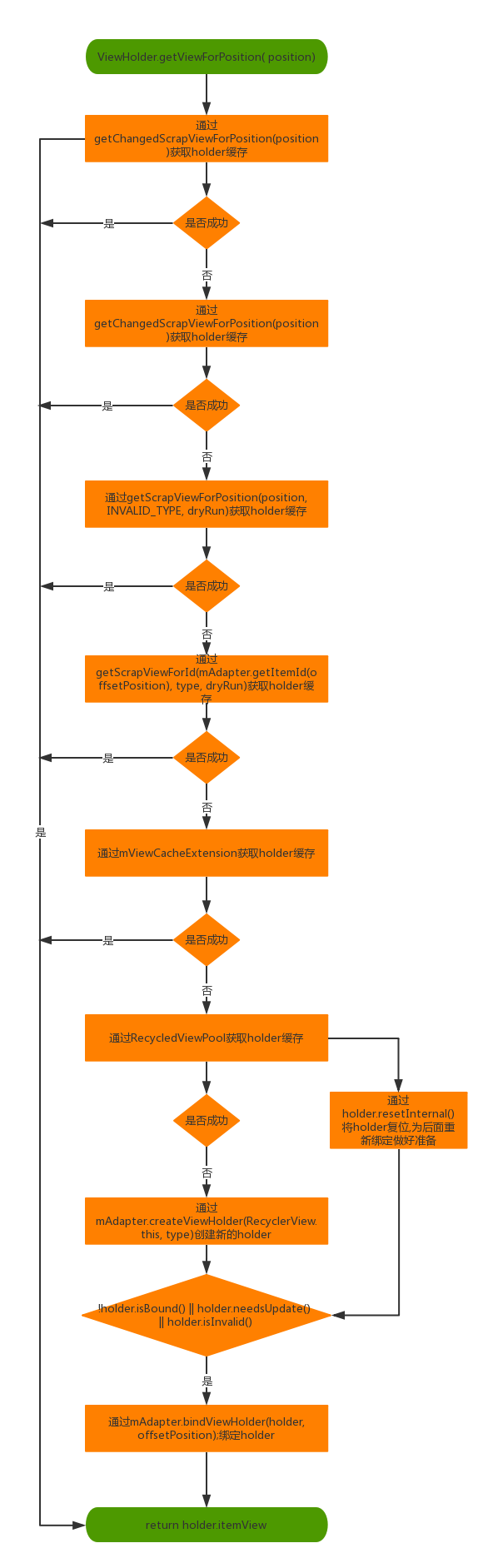
首先需要说明的是,ListView缓存的是View,而RecycleView缓存的ViewHolder。
RecycleView查找View是从getViewForPosition开始的:
public View getViewForPosition(int position) {
return getViewForPosition(position, false);
}
RecyleView的缓存会设计到好几层:
- mChangedScrap
- mAttachedScrap
- mCachedViews
- mViewCacheExtension
- mRecyclerPool

- ListView的mActiveViews和RecycleView的mAttachedScrap功能相似,意义在于快速重用屏幕上可见的列表项ItemView,而不需要重新createView和bindView;
- ListView的mScrapView和RecycleView的(mCachedViews + mReyclerViewPool)功能相似,意义在于缓存离开屏幕的ItemView,目的是让即将进入屏幕的ItemView重用.
- mReyclerViewPool的优势在于可以供多个RecyclerView共同使用。
具体会经过以下的几个步骤
步骤1:getChangedScrapViewForPosition
getView的第一步是从mChangedScrap获取holder缓存。具体的实现会经过2步:
- 通过mChangedScrap匹配 position获取holder缓存
- 通过mChangedScrap匹配id获取holder缓存
ViewHolder getChangedScrapViewForPosition(int position) {
// If pre-layout, check the changed scrap for an exact match.
final int changedScrapSize;
if (mChangedScrap == null || (changedScrapSize = mChangedScrap.size()) == 0) {
return null;
}
// find by position
for (int i = 0; i < changedScrapSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mChangedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
// find by id
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
if (offsetPosition > 0 && offsetPosition < mAdapter.getItemCount()) {
final long id = mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition);
for (int i = 0; i < changedScrapSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mChangedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getItemId() == id) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
步骤2:getScrapViewForPosition
第二步就是查找废弃的viewholder了,主要是通过以下3步:
- 从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配position获取holder缓存
- 通过ChildHelper找到隐藏但是没有被移除的View,通过getChildViewHolderInt(view)方法获取holder缓存
- 从mCachedViews中通过匹配position获取holder缓存
ViewHolder getScrapViewForPosition(int position, int type, boolean dryRun) {
final int scrapCount = mAttachedScrap.size();
// 第一步查找:mAttachedScrap
for (int i = 0; i < scrapCount; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mAttachedScrap.get(i);
if (!holder.wasReturnedFromScrap() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position
&& !holder.isInvalid() && (mState.mInPreLayout || !holder.isRemoved())) {
if (type != INVALID_TYPE && holder.getItemViewType() != type) {
Log.e(TAG, "Scrap view for position " + position + " isn't dirty but has" +
" wrong view type! (found " + holder.getItemViewType() +
" but expected " + type + ")");
break;
}
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
return holder;
}
}
// 第二步查找:通过ChildHelper找到隐藏但是没有被移除的View,通过getChildViewHolderInt(view)方法获取holder缓存
if (!dryRun) {
View view = mChildHelper.findHiddenNonRemovedView(position, type);
if (view != null) {
// This View is good to be used. We just need to unhide, detach and move to the
// scrap list.
final ViewHolder vh = getChildViewHolderInt(view);
mChildHelper.unhide(view);
int layoutIndex = mChildHelper.indexOfChild(view);
if (layoutIndex == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
throw new IllegalStateException("layout index should not be -1 after "
+ "unhiding a view:" + vh);
}
mChildHelper.detachViewFromParent(layoutIndex);
scrapView(view);
vh.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP
| ViewHolder.FLAG_BOUNCED_FROM_HIDDEN_LIST);
return vh;
}
}
// 第三步查找:mCachedViews
final int cacheSize = mCachedViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cacheSize; i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = mCachedViews.get(i);
// invalid view holders may be in cache if adapter has stable ids as they can be
// retrieved via getScrapViewForId
if (!holder.isInvalid() && holder.getLayoutPosition() == position) {
if (!dryRun) {
mCachedViews.remove(i);
}
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getScrapViewForPosition(" + position + ", " + type +
") found match in cache: " + holder);
}
return holder;
}
}
return null;
}
步骤3:getScrapViewForId
getScrapViewForId方法内部主要通过2种方法获取holder缓存。
- 从mAttachedScrap中通过匹配id获取holder缓存
- 从mCachedViews中通过匹配id获取holder缓存
ViewHolder getScrapViewForId(long id, int type, boolean dryRun) {
// Look in our attached views first
final int count = mAttachedScrap.size();
for (int i = count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final ViewHolder holder = mAttachedScrap.get(i);
if (holder.getItemId() == id && !holder.wasReturnedFromScrap()) {
if (type == holder.getItemViewType()) {
holder.addFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_RETURNED_FROM_SCRAP);
if (holder.isRemoved()) {
// this might be valid in two cases:
// > item is removed but we are in pre-layout pass
// >> do nothing. return as is. make sure we don't rebind
// > item is removed then added to another position and we are in
// post layout.
// >> remove removed and invalid flags, add update flag to rebind
// because item was invisible to us and we don't know what happened in
// between.
if (!mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder.setFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE, ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE |
ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID | ViewHolder.FLAG_REMOVED);
}
}
return holder;
} else if (!dryRun) {
// if we are running animations, it is actually better to keep it in scrap
// but this would force layout manager to lay it out which would be bad.
// Recycle this scrap. Type mismatch.
mAttachedScrap.remove(i);
removeDetachedView(holder.itemView, false);
quickRecycleScrapView(holder.itemView);
}
}
}
// Search the first-level cache
final int cacheSize = mCachedViews.size();
for (int i = cacheSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final ViewHolder holder = mCachedViews.get(i);
if (holder.getItemId() == id) {
if (type == holder.getItemViewType()) {
if (!dryRun) {
mCachedViews.remove(i);
}
return holder;
} else if (!dryRun) {
recycleCachedViewAt(i);
}
}
}
return null;
}
步骤4:ViewCacheExtension
这个类是给应用开发者实现的,就是实现自己的缓存。是一个抽象类,具体的显示由继承者实现。
abstract public View getViewForPositionAndType(Recycler recycler, int position, int type);
步骤5:RecycledViewPool
通过RecyclerView 的ViewHolder缓存池获取holder。
if (holder == null) {
// fallback to recycler
// try recycler.
// Head to the shared pool.
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getViewForPosition(" + position + ") fetching from shared " + "pool");
}
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
if (holder != null) {
holder.resetInternal();
if (FORCE_INVALIDATE_DISPLAY_LIST) {
invalidateDisplayListInt(holder);
}
}
}
// getRecycledView
public ViewHolder getRecycledView(int viewType) {
final ArrayList<ViewHolder> scrapHeap = mScrap.get(viewType);
if (scrapHeap != null && !scrapHeap.isEmpty()) {
final int index = scrapHeap.size() - 1;
final ViewHolder scrap = scrapHeap.get(index);
scrapHeap.remove(index);
return scrap;
}
return null;
}
步骤6:创建新的holder
在经过上面那么多步骤还没有找到缓存的holder时,就会创建新的holder。
if (holder == null) {
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "getViewForPosition created new ViewHolder");
}
}
// createViewHolder
public final VH createViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
TraceCompat.beginSection(TRACE_CREATE_VIEW_TAG);
final VH holder = onCreateViewHolder(parent, viewType);
holder.mItemViewType = viewType;
TraceCompat.endSection();
return holder;
}
// ViewHolder
public abstract VH onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType);
整体的流程如下:
RecycleView的局部刷新
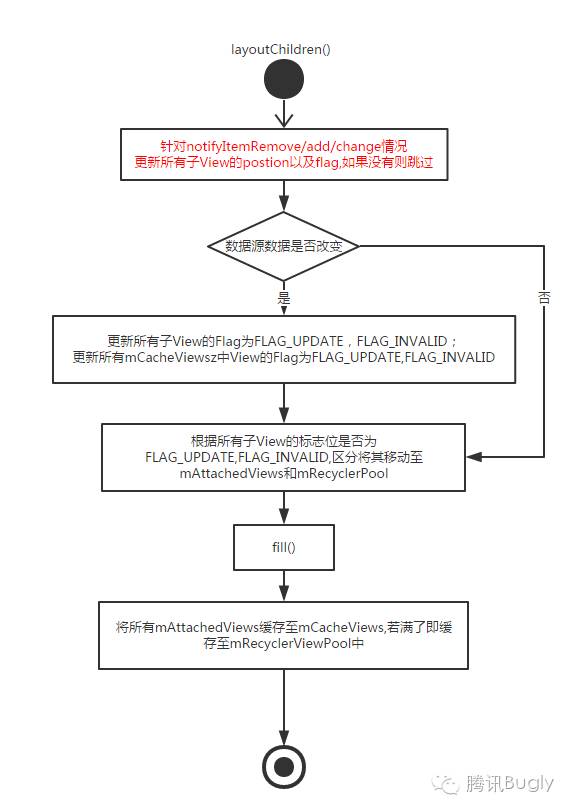
局部刷新不管是调用notifyXXX()什么方法,最终都是会调用requestLayout(),使整个RecycleView完成重绘。
void dispatchLayout() {
...
mState.mIsMeasuring = false;
if (mState.mLayoutStep == State.STEP_START) {
dispatchLayoutStep1();
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else if (mAdapterHelper.hasUpdates() || mLayout.getWidth() != getWidth() ||
mLayout.getHeight() != getHeight()) {
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
dispatchLayoutStep2();
} else {
mLayout.setExactMeasureSpecsFrom(this);
}
dispatchLayoutStep3();
}
dispatchLayoutStep1()
用来记录RecycleView刷新前列表项的各种信息,存放在ViewInfoStore对象中,用于动画相关的操作??
if (mState.mRunSimpleAnimations) {
...
mViewInfoStore.addToOldChangeHolders(key, holder);
...
}
if (mState.mRunPredictiveAnimations) {
...
if (wasHidden) {
recordAnimationInfoIfBouncedHiddenView(viewHolder, animationInfo);
} else {
mViewInfoStore.addToAppearedInPreLayoutHolders(viewHolder, animationInfo);
}
...
}
dispatchLayoutStep2()
真正的测量布局,可能会被调用多次,核心的方法是:onLayoutChildren()。
dispatchLayoutStep3()
最后一步是为了执行动画保存view的信息,在合适的时机触发动画,并做一些清理操作。
关于onLayoutChildren()
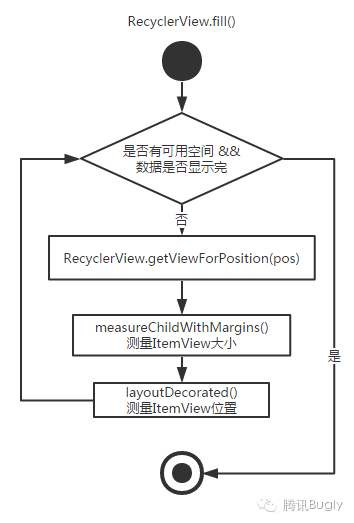
而核心的方法就是fill(),fill的流程如下: