WindowManager技术总结
Window窗口是怎么管理的?

添加一个窗口的过程就是WMS为窗口分配一块Surface,用来承载window,一块块的Surface在WMS的管理下有序的排列在屏幕上。
在应用层开发时,我们只操作UI层,通过WindowManager来操作Window,最终调到WMS。WMS是在一个单独的进程中,内部采用IPC进行交互。
窗口的分类
- 应用窗口:应用窗口对应着一个Activity/Fragment
- 子窗口:子窗口不能单独存在,需要依附在特定的父窗口(如应用窗口、系统窗口),典型的如Dialog就是子窗口
- 系统窗口:系统窗口就要涉及到权限了(toast也是系统窗口)
窗口是有层级的,层级大的窗口会覆盖层级小的窗口,具体分布如下:

而层级的定义就是通过WindowManager.LayoutParams的type参数。
WindowManager的具体实现
WindowManager.java
WindowManager是个接口,主要的代码是LayoutParams。它继承了ViewManager接口类。而viewManager接口是很多View类的父类。
public interface ViewManager{
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void removeView(View view);
}
WindowManager就是主要通过这3个方法完成对窗口的控制。WindowManager的具体实现类是WindowManagerImpl。
addView
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
applyDefaultToken()是当没有token是,自动添加上一个默认的token【token其实就是IBinder】。
getDisplay()是获取Display类,每个窗口都需要绑定到特定的Display中,即窗口和Display对象是一一对应的。
Display类
提供逻辑显示区域大小、密度等相关信息。
应用程序显示区域指定的部分可能包含一个应用程序窗口的显示,排除系统装饰。应用程序显示区域可能比真正的显示区域要小,因为系统减去所需的空间装饰元素状态栏等。可以使用一下方法来获取应用程序显示区域的信息: getSize(Point), getRectSize(Rect), getHeight() 和getMetrics(DisplayMetrics)
Display类是无法自己实例化的,需要通过getService获取。
WindowManager windowmanager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
windowmanager.getDefaultDisplay()
DisplayMetrics类
为一个描述显示区域信息的结构体类,包括大小、密度、字体缩放等。
它需要依托Display类完成实例化。
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
个人感觉DisplayMetrics应该是对Display类的一种补充。
addView的核心代码:
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
synchronized (mLock) {
final int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
}
throw e;
}
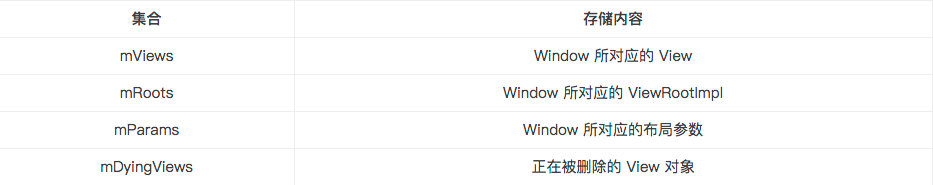
几个重要的集合:
private final ArrayList<View> mViews = new ArrayList<View>();
private final ArrayList<ViewRootImpl> mRoots = new ArrayList<ViewRootImpl>();
private final ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams> mParams = new ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams>();
private final ArraySet<View> mDyingViews = new ArraySet<View>();
他们的具体含义:
首先创建ViewRootImpl实例对象,就是最顶级的ViewGroup,承载我们自己的View。
最后调用setView()将view绘制到界面上。它的核心代码:
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
mForceDecorViewVisibility = (mWindowAttributes.privateFlags
& PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY) != 0;
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
首先调用requestLayout()方法。
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
然后调用addToDipsplay。
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams, attrs, int viewVisibility,
int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, InputChannel outInputChannel){
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outContentInsets, outInputChannel);
}
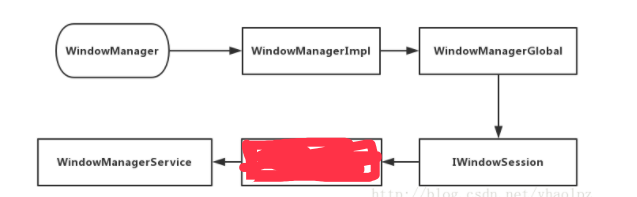
最终,Window的添加请求移交 WindowManagerService 手上了,具体的流程如下:
updateViewLayout
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
mParams.remove(index);
mParams.add(index, wparams);
root.setLayoutParams(wparams, false);
}
}
这里主要是调用到scheduleTraversals()方法。
removeView
public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView();
removeViewLocked(index, immediate);
if (curView == view) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Calling with view " + view
+ " but the ViewAncestor is attached to " + curView);
}
}